E D U C A T I O N
STROKE
S T R O K E
Stroke: Care Instructions
Your Care Instructions
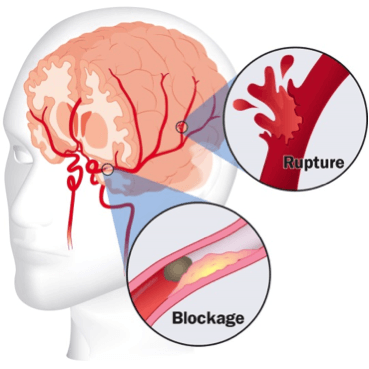
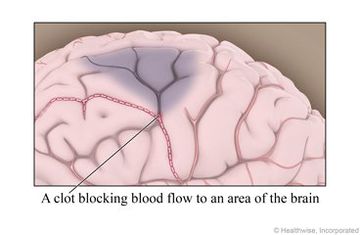
You have had a stroke. This means that the blood flow to a part of your brain was blocked for some time, which damages the nerve cells in that part of the brain. The part of your body controlled by that part of your brain may not function properly now.
The brain is an amazing organ that can heal itself to some degree. The stroke you had damaged part of your brain. But other parts of your brain may take over in some way for the damaged areas. You have already started this process.
Your doctor will talk with you about what you can do to prevent another stroke. High blood pressure, high cholesterol, and diabetes are all risk factors for stroke. If you have any of these conditions, work with your doctor to make sure they are under control. Other risk factors for stroke include being overweight, smoking, and not getting regular exercise.
Going home may be hard for you and your family. The more you can try to do for yourself, the better. Remember to take each day one at a time.
How can you care for yourself at home?
- Enter a stroke rehabilitation (rehab) program, if your doctor recommends it. Physical, speech, and occupational therapies can help you manage bathing, dressing, eating, and other basics of daily living.
- Do not drive until your doctor says it is okay.
- It is normal to feel sad or depressed after a stroke. If these feelings last, talk to your doctor.
- If you are having problems with urine leakage, go to the bathroom at regular times, including when you first wake up and at bedtime. Also, limit fluids after dinner.
- If you are constipated, drink plenty of fluids, enough so that your urine is light yellow or clear like water. If you have kidney, heart, or liver disease and have to limit fluids, talk with your doctor before you increase the amount of fluids you drink. Set up a regular time for using the toilet.
- If you continue to have constipation, your doctor may suggest using a bulking agent, such as Metamucil, or a stool softener, laxative, or enema.
Medicines
- Take your medicines exactly as prescribed. Call your doctor if you think you are having a problem with your medicine. You may be taking several medicines. ACE (angiotensin-converting enzyme) inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs), beta-blockers, diuretics (water pills), and calcium channel blockers control your blood pressure. Statins help lower cholesterol. Your doctor may also prescribe medicines for depression, pain, sleep problems, anxiety, or agitation.
- If your doctor has given you a blood thinner to prevent another stroke, be sure you get instructions about how to take your medicine safely. Blood thinners can cause serious bleeding problems.
- Do not take any over-the-counter medicines or herbal products without talking to your doctor first.
- If you take birth control pills or hormone therapy, talk to your doctor about whether they are right for you.
For family members and caregivers
- Make the home safe. Set up a room so that your loved one does not have to climb stairs. Be sure the bathroom is on the same floor. Move throw rugs and furniture that could cause falls. Make sure that the lighting is good. Put grab bars and seats in tubs and showers.
- Find out what your loved one can do and what he or she needs help with. Try not to do things for your loved one that your loved one can do on his or her own. Help him or her learn and practice new skills.
- Visit and talk with your loved one often. Try doing activities together that you both enjoy, such as playing cards or board games. Keep in touch with your loved one's friends as much as you can. Encourage them to visit.
- Take care of yourself. Do not try to do everything yourself. Ask other family members to help. Eat well, get enough rest, and take time to do things that you enjoy. Keep up with your own doctor visits, and make sure to take your medicines regularly. Get out of the house as much as you can. Join a local support group. Find out if you qualify for home health care visits to help with rehab or for adult day care.
Call 911 anytime you think you may need emergency care. For example, call if:
You have signs of another stroke. These may include:
- Sudden numbness, tingling, weakness, or loss of movement in your face, arm, or leg, especially on only one side of your body.
- Sudden vision changes.
- Sudden trouble speaking.
- Sudden confusion or trouble understanding simple statements.
- Sudden problems with walking or balance.
- A sudden, severe headache that is different from past headaches.
Learning About FAST: Stroke Warning Sign
What is FAST?
FAST is a simple way to remember the main symptoms of stroke. Recognizing these symptoms helps you know when to call for medical help.
FAST stands for:
- Face drooping.
- Arm weakness.
- Speech difficulty.
- Time to call 911.
What happens when you have a stroke?
A stroke occurs when a blood vessel to the brain bursts or is blocked by a blood clot. Within minutes, the nerve cells in that part of the brain die. As a result, the part of the body controlled by those cells cannot work properly.
The effects of a stroke may range from mild to severe. They may get better, or they may last the rest of your life. A stroke can affect vision, speech, behavior, thought processes, and your ability to move.
It can cause symptoms that may include:
- Sudden numbness, tingling, weakness, or loss of movement in your face, arm, or leg, especially on only one side of your body.
- Sudden vision changes.
- Sudden trouble speaking.
- Sudden confusion or trouble understanding simple statements.
- Sudden problems with walking or balance.
- A sudden, severe headache that is different from past headaches.
Why is it important to get help FAST?
Quick treatment may save your life. And it may reduce the damage in your brain so that you have fewer problems after the stroke.
LEARN MORE
When you know the FAST symptoms, you will know when it's important to call for medical help.
Care instructions adapted under license by Alliance In Health Diabetes Control Center. This care instruction is for use with your licensed healthcare professional. If you have questions about a medical condition or this instruction, always ask your healthcare professional. Healthwise, Incorporated disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information.