D I A B E T E S
Learning About Type 2 Diabetes
What is type 2 diabetes?
Type 2 diabetes is a disease that develops when the body's tissues cannot use insulin properly. Over time, the pancreas cannot make enough insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps the body's cells use sugar (glucose) for energy. It also helps the body store extra sugar in muscle, fat, and liver cells.
- Insulin is a hormone that helps your body use sugar from your food as energy. Type 2 diabetes happens when your body can't use insulin the right way or when the pancreas can't make enough of it. If you don't have enough insulin, too much sugar stays in your blood.
- Without insulin, the sugar cannot get into the cells to do its work. It stays in the blood instead. This can cause high blood sugar levels. A person has diabetes when the blood sugar stays too high too much of the time. Over time, diabetes can lead to diseases of the heart, blood vessels, nerves, kidneys, and eyes.
- If you are overweight, get little or no exercise, or have type 2 diabetes in your family, you are more likely to have problems with the way insulin works in your body.
- You may be able to control your blood sugar by losing weight, eating a healthy diet, and getting daily exercise. You may also have to take insulin or other diabetes medicine.
- Type 2 diabetes is a lifelong disease, But it can be prevented or delayed with a healthy lifestyle, which includes staying at a healthy weight, making smart food choices, and getting regular exercise.
What can you expect with type 2 diabetes?
You'll keep hearing about how important it is to keep your blood sugar within a target range. That's because over time, high blood sugar can lead to serious problems. It can:
- Harm your eyes, nerves, and kidneys.
- Damage your blood vessels, leading to heart disease and stroke.
- Reduce blood flow and cause nerve damage to parts of your body, especially your feet. This can cause slow healing and pain when you walk.
- An immune system that's weak and less able to fight infections.
- When people hear the word "diabetes," they often think of problems like these. But daily care and treatment can help prevent or delay these problems. The goal is to keep your blood sugar in a target range. That's the best way to reduce your chance of having more problems from diabetes.
What are the symptoms?
You experience most symptoms of type 2 diabetes when your blood sugar is either too high or too low.
The most common symptoms of high blood sugar include:
- Thirst.
- Frequent urination.
- Weight loss.
- Blurry vision.
The symptoms of low blood sugar include:
- Sweating.
- Shakiness.
- Weakness.
- Hunger.
- Confusion.
How can you prevent type 2 diabetes?
The best way to prevent or delay type 2 diabetes is to adopt healthy habits, which include:
- Staying at a healthy weight.
- Exercising regularly.
- Eating healthy foods.
- How is type 2 diabetes treated?
- If you have type 2 diabetes, here are the most important things you can do.
Take your diabetes medicines.
Check your blood sugar as often as your doctor recommends. Also, get a hemoglobin A1c test at least every 6 months. Try to eat a variety of foods and to spread carbohydrate throughout the day. Carbohydrate raises blood sugar higher and more quickly than any other nutrient does. Carbohydrate is found in sugar, breads and cereals, fruit, starchy vegetables such as potatoes and corn, and milk and yogurt. Get at least 30 minutes of exercise on most days of the week. Walking is a good choice.
You also may want to do other activities, such as running, swimming, cycling, or playing tennis or team sports. See your doctor for checkups and tests on a regular schedule. If you have high blood pressure or high cholesterol, take the medicines as prescribed by your doctor. Do not smoke. Smoking can make health problems worse. This includes problems you might have with type 2 diabetes. If you need help quitting, talk to your doctor about stop-smoking programs and medicines. These can increase your chances of quitting for good. Follow-up care is a key part of your treatment and safety. Be sure to make and go to all appointments, and call your doctor if you are having problems. It's also a good idea to know your test results and keep a list of the medicines you take.
Follow-up care is a key part of your treatment and safety.
Be sure to make and go to all appointments, and call your doctor if you are having problems. It's also a good idea to know your test results and keep a list of the medicines you take.
Care instructions adapted under license by Alliance In Health Diabetes Control Center. This care instruction is for use with your licensed healthcare professional. If you have questions about a medical condition or this instruction, always ask your healthcare professional. Healthwise, Incorporated disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information.
LEARN MORE
U N D E R S T A N D I N G D I A B E T E S
Understanding Diabetes
Information You Should Know
Simply stated, patients with diabetes are at greater risk for cardiovascular disease.
REQUEST AN APPOINTMENT
D I A B E T E S R I S K C A L C
Type 2 Diabetes Self-Assessment
Take this quick and simple test to find out if you're at risk of type 2 diabetes. Please note, this tool may not be accurate for anyone undergoing treatment for diabetes.
C A R E I N S T R U C T I O N S
Type 2 Diabetes: Care Instructions
Your Care Instructions.
Type 2 diabetes is a disease that develops when the body's tissues cannot use insulin properly. Over time, the pancreas cannot make enough insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps the body's cells use sugar (glucose) for energy. It also helps the body store extra sugar in muscle, fat, and liver cells.
Without insulin, the sugar cannot get into the cells to do its work. It stays in the blood instead. This can cause high blood sugar levels. A person has diabetes when the blood sugar stays too high too much of the time. Over time, diabetes can lead to diseases of the heart, blood vessels, nerves, kidneys, and eyes.
You may be able to control your blood sugar by losing weight, eating a healthy diet, and getting daily exercise. You may also have to take pills or insulin shots (or both).
Follow-up care is a key part of your treatment and safety. Be sure to make and go to all appointments, and call your doctor if you are having problems. It's also a good idea to know your test results and keep a list of the medicines you take.
Care instructions adapted under license by Alliance In Health Diabetes Control Center. This care instruction is for use with your licensed healthcare professional. If you have questions about a medical condition or this instruction, always ask your healthcare professional. Healthwise, Incorporated disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information.
LEARN MORE
O R A L T H E R A P Y
Oral Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes: Care Instructions
Your Care Instructions.
People with type 2 diabetes have two problems that lead to high blood sugar. Their bodies don't make enough insulin to control their blood sugar. And their bodies don't respond well to insulin when it is present. Oral medicines for type 2 diabetes can raise your insulin. They also help your body use insulin better. You take these drugs by mouth. Sometimes they are combined with insulin.
Some examples of these medicines are:
Sulfonylureas
These help the body make more insulin. They include glipizide and glyburide.
Meglitinides
These also help your body make insulin. They include nateglinide and repaglinide.
Metformin
This lowers how much glucose your liver makes. And it helps you respond better to insulin.
Thiazolidinediones
These also reduce the amount of blood glucose. They also help you respond better to insulin. These medicines include pioglitazone and rosiglitazone.
Alpha-glucosidase Inhibitors
These keep starches from breaking down. This means that they lower the amount of glucose absorbed when you eat. They include acarbose and miglitol.
DPP-4 Inhibitors
These help the body make more insulin. They also help the body make less of a hormone that raises blood sugar. They include linagliptin, saxagliptin, and sitagliptin.
Sodium Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors
These help to remove extra glucose through your urine. They may also help some people lose weight. These medicines are also called SGLT2 inhibitors. They include canagliflozin, dapagliflozin, and empagliflozin.
You may take one or more of these drugs. You and your doctor can choose the best ones for you. If pills can't control your blood sugar, you may need to use medicine that you take as a shot. These include amylinomimetics, incretin mimetics, and insulin.
You may need to use insulin for a short time if you get sick or need surgery. Drugs that you take by mouth may not control blood sugar when your body is stressed.
Follow-up care is a key part of your treatment and safety. Be sure to make and go to all appointments, and call your doctor if you are having problems. It's also a good idea to know your test results and keep a list of the medicines you take.
Care instructions adapted under license by Alliance In Health Diabetes Control Center. This care instruction is for use with your licensed healthcare professional. If you have questions about a medical condition or this instruction, always ask your healthcare professional. Healthwise, Incorporated disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information.
LEARN MORE
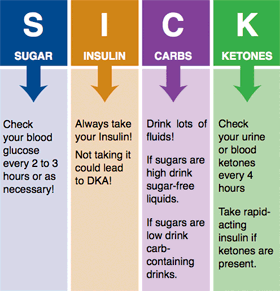
S I C K - D A Y
Diabetes Sick-Day Plan: Care Instructions
Your Care Instructions.
If you have diabetes, many other illnesses can make your blood sugar go up. This can be dangerous. When you are sick with the flu or another illness, your body releases hormones to fight infection. These hormones raise blood sugar levels and make it hard for insulin or other medicines to lower your blood sugar.
Work with your doctor to make a plan for what to do on days when you are sick.
Follow-up care is a key part of your treatment and safety. Be sure to make and go to all appointments, and call your doctor if you are having problems. It's also a good idea to know your test results and keep a list of the medicines you take.
Care instructions adapted under license by Alliance In Health Diabetes Control Center. This care instruction is for use with your licensed healthcare professional. If you have questions about a medical condition or this instruction, always ask your healthcare professional. Healthwise, Incorporated disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information.
LEARN MORE
P E R S O N A L I Z E D E D .
Diabetes Educators Available to Guide You
There is a lot to know when you or a loved one has diabetes. Our diabetes educators, available at all AIHDCC locations, are there to help you with getting the information you need. Be sure to take advantage of this opportunity during your visit with the provider to find out how to:
- Monitor your glucose including how to choose the best testing devices and process for you.
- Use diabetes medications
- Maintain foot health
- Know the symptoms of eye conditions caused by diabetes
- Plan meals
- One-on-one sessions are available to help you and your family design a diabetes-management plan tailored to your individual needs. Plus, this service is covered by Medicare and other insurance providers.
Learn more about what a diabetes educator can do for you and then be sure to include a session with your next visit.